Clavicle Fracture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A clavicle fracture, also known as a broken collarbone, is a bone fracture of the
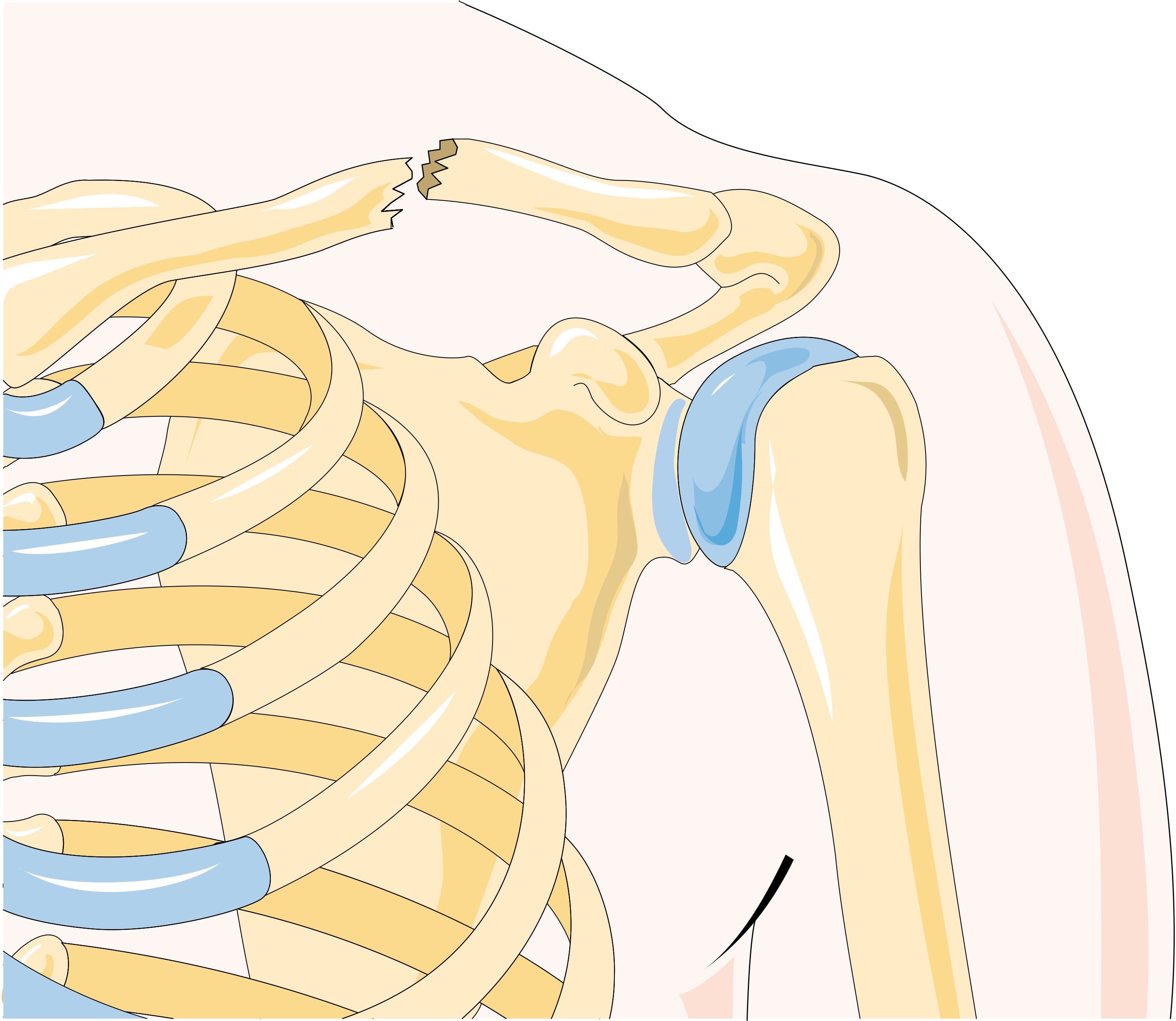 The clavicle is the bone that connects the trunk of the body to the arm, and it is located directly above the
The clavicle is the bone that connects the trunk of the body to the arm, and it is located directly above the
 For breaks in the middle of the clavicle in children surgery resulted in faster recover but more complications. The evidence for different types of surgery for breaks of the middle part of the clavicle is poor as of 2015.
Surgery may be considered when one or more of the following is presents
* Comminution with separation (bone is broken into multiple pieces)
* Skin penetration (open fracture)
* Associated nervous and vascular trauma (brachial plexus or supraclavicular nerves)
* Nonunion after several months (3–6 months, typically)
* Displaced distal third fractures (high risk of nonunion)
* Although shortening (as a result of overlap of fracture ends) has often been suggested as an indication for surgery, a review found that people treated without surgery for shortening of mid shaft clavicle fractures did not affect outcomes.
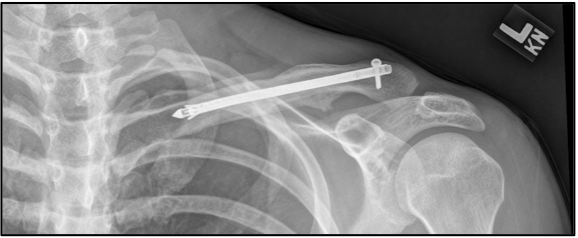
A discontinuity in the bone shape often results from a clavicular fracture, visible through the skin, if not treated with surgery. Surgical procedures often call for open reduction internal latefixation where an anatomically shaped titanium or steel plate is affixed along the superior aspect of the bone by several screws. In some cases, the plate is removed after healing due to discomfort, to avoid tissue aggravation, osteolysis or subacromial impingement. This is especially important with a special type of fixation plate called hook plate. With anatomical plates plate removal is considered an elective procedure that is rarely necessary. An alternative to plate fixation is elastic TEN intramedullary nailing. These devices are implanted within the clavicle's canal to support the bone from the inside. Typical surgical complications are infection, neurological symptoms distal the incision (sometimes to the extremity), and
For breaks in the middle of the clavicle in children surgery resulted in faster recover but more complications. The evidence for different types of surgery for breaks of the middle part of the clavicle is poor as of 2015.
Surgery may be considered when one or more of the following is presents
* Comminution with separation (bone is broken into multiple pieces)
* Skin penetration (open fracture)
* Associated nervous and vascular trauma (brachial plexus or supraclavicular nerves)
* Nonunion after several months (3–6 months, typically)
* Displaced distal third fractures (high risk of nonunion)
* Although shortening (as a result of overlap of fracture ends) has often been suggested as an indication for surgery, a review found that people treated without surgery for shortening of mid shaft clavicle fractures did not affect outcomes.
A discontinuity in the bone shape often results from a clavicular fracture, visible through the skin, if not treated with surgery. Surgical procedures often call for open reduction internal latefixation where an anatomically shaped titanium or steel plate is affixed along the superior aspect of the bone by several screws. In some cases, the plate is removed after healing due to discomfort, to avoid tissue aggravation, osteolysis or subacromial impingement. This is especially important with a special type of fixation plate called hook plate. With anatomical plates plate removal is considered an elective procedure that is rarely necessary. An alternative to plate fixation is elastic TEN intramedullary nailing. These devices are implanted within the clavicle's canal to support the bone from the inside. Typical surgical complications are infection, neurological symptoms distal the incision (sometimes to the extremity), and
Details from AAOS
{{DEFAULTSORT:Clavicle Fracture Bone fractures Injuries of shoulder and upper arm Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the r ...
. Symptoms typically include pain at the site of the break and a decreased ability to move the affected arm. Complications can include a collection of air in the pleural space
The pleural cavity, pleural space, or interpleural space is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication bet ...
surrounding the lung (pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve i ...
), injury to the nerves or blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s in the area, and an unpleasant appearance.
It is often caused by a fall onto a shoulder, outstretched arm, or direct trauma. The fracture can also occur in a baby during childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glob ...
. The middle section of the clavicle is most often involved. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and confirmed with X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s.
Clavicle fractures are typically treated by putting the arm in a sling for one or two weeks. Pain medication such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) may be useful. It can take up to five months for the strength of the bone to return to normal. Reasons for surgical repair include an open fracture
An open fracture, also called a compound fracture, is a type of bone fracture in orthopedics that is frequently caused by high energy trauma. It is a bone fracture, also known as a broken bone, associated with a break in the skin continuity which ...
, involvement of the nerves or blood vessels, or shortening of the clavicle by more than 1.5 cm in a young person.
Clavicle fractures most commonly occur in people under the age of 25 and those over the age of 70. Among the younger group males are more often affected than females. In adults they make up about 5% of all fractures while in children they represent about 13% of fractures.
Signs and symptoms
* Pain, particularly with arm movement or on the front part of upper chest * Swelling * Often, after the swelling has subsided, the fracture can be felt through theskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
.
* Sharp pain when any movement is made
* Referred pain
Referred pain, also called reflective pain, is pain perceived at a location other than the site of the painful stimulus. An example is the case of angina pectoris brought on by a myocardial infarction (heart attack), where pain is often felt in ...
: dull to extreme ache in and around clavicle area, including surrounding muscles
* Possible nausea, dizziness, and/or spotty vision due to extreme pain
Mechanism
Clavicle fractures are commonly known as a breaking of the collarbone, and they are usually a result of injury or trauma. The most common type of fracture occurs when a person falls horizontally on the shoulder or with an outstretched hand. A direct hit to the collarbone can also cause a break. In most cases, the direct hit occurs from the lateral side towards the medial side of the bone. The muscles involved in clavicle fractures include the deltoid,trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports th ...
, subclavius
The subclavius is a small triangular muscle, placed between the clavicle and the first rib. Along with the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles, the subclavius muscle makes up the anterior axioappendicular muscles, also known as anter ...
, sternocleidomastoid, and sternohyoid
The sternohyoid muscle is a thin, narrow muscle attaching the hyoid bone to the sternum. It is one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles. It is supplied by the ansa cervicalis. It depresses the hyoid bone.
Structure
The sternoh ...
. The ligaments involved include the conoid ligament
The conoid ligament is the posterior and medial fasciculus of the coracoclavicular ligament. It is formed by a dense band of fibers, conical in form, with its base directed upward.
It is attached by its apex to a rough impression at the base of th ...
and trapezoid ligament
The trapezoid ligament is a ligament connecting the coracoid process of the scapula (the shoulder blade) to the trapezoid line of the clavicle (collarbone). It is an anterior and lateral fasciculus, and is broad, thin, and quadrilateral. Its ant ...
. Incidents that may lead to a clavicle fracture include automobile accidents, biking accidents (especially common in mountain biking), horizontal falls on the shoulder joint, or contact sports such as football, rugby, hurling, or wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat ...
.
It is most often fractured in the middle third of its length which is its weakest point. The lateral fragment of the clavicle during a fracture is depressed by the weight of the arm and is pulled downward by the strong abductor muscles of the shoulder joint, especially the deltoid. The part of the clavicle near the center of the body is tilted upwards by the sternocleidomastoid muscle
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the access ...
. Children and infants are particularly prone to it. Newborns often present clavicle fractures following a difficult delivery.
After fracture of the clavicle, the sternocleidomastoid muscle elevates the medial fragment of the bone. The trapezius muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the ...
is unable to hold up the distal fragment owing to the weight of the upper limb, thus the shoulder droops. The adductor muscles of the arm, such as the pectoralis major, may pull the distal fragment medially, causing the bone fragments to override.
Anatomy
 The clavicle is the bone that connects the trunk of the body to the arm, and it is located directly above the
The clavicle is the bone that connects the trunk of the body to the arm, and it is located directly above the first rib
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi ...
. A clavicle is located on each side of the front, upper part of the chest. The clavicle consists of a medial end, a shaft, and a lateral end. The medial end connects with the manubrium of the sternum and gives attachments to the fibrous capsule of the sternoclavicular joint
The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a synovial saddle joint between the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle, as well as the first rib. The joint possesses a joint capsule, and an articular disk, and is reinfo ...
, articular disc, and interclavicular ligament
The interclavicular ligament is a flattened band, which varies considerably in form and size in different individuals, it passes in a curved direction from the upper part of the sternal end of one clavicle to that of the other, and is also attache ...
. The lateral end connects at the acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The ac ...
of the scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eith ...
which is referred to as the acromioclavicular joint
The acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint, is a joint at the top of the shoulder. It is the junction between the acromion (part of the scapula that forms the highest point of the shoulder) and the clavicle. It is a plane synovial joint.
Structure ...
. The clavicle forms a slight S-shaped curve where it curves from the sternal end laterally and anteriorly for near half its length, then forming a posterior curve to the acromion of the scapula.
Diagnosis
The basic method to check for a clavicle fracture is by an X-ray of the clavicle to determine the fracture type and extent of injury. In former times, X-rays were taken of both clavicle bones for comparison purposes. Due to the curved shape in a tilted plane X-rays are typically oriented with ~15° upwards facing tilt from the front. In more severe cases, a computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is taken. However, the standard method of diagnosis throughultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
imaging performed in the emergency room may be equally accurate in children.
Treatment
Medication may be prescribed for pain. It is unclear if surgery or conservative management is superior. Antibiotics and tetanus vaccination may be used if the bone breaks through the skin however this is uncommon. Often, they are treated without surgery. In severe cases, surgery may be done.Nonoperative
The arm is usually supported by an external immobilizer to keep the joint stable and decrease the risk of further damage. The two most common types of fixation are the figure-of-eight splint that wraps the shoulders to keep them forced back and a simple broad arm sling (which supports the weight of the arm). The primary indication is pain relief. Type of sling used does not seem to affect the results as far as healing is concerned but patient satisfaction is lower with the figure-of-eight bandage. No difference in functional outcome has been reported between the two types of immobilization. Current practice for simple fractures without great displacement is generally to provide a sling, and pain relief, and to allow the bone to heal itself, monitoring progress with X-rays every week or few weeks if necessary. Surgery is employed in 5–10% of cases. However, a meta-analysis of 2 144 midshaft clavicle fractures supports primary plate fixation of completely displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in active adult patients. If the fracture is at the lateral end, the risk of nonunion is greater than if the fracture is of the shaft.Surgical
 For breaks in the middle of the clavicle in children surgery resulted in faster recover but more complications. The evidence for different types of surgery for breaks of the middle part of the clavicle is poor as of 2015.
Surgery may be considered when one or more of the following is presents
* Comminution with separation (bone is broken into multiple pieces)
* Skin penetration (open fracture)
* Associated nervous and vascular trauma (brachial plexus or supraclavicular nerves)
* Nonunion after several months (3–6 months, typically)
* Displaced distal third fractures (high risk of nonunion)
* Although shortening (as a result of overlap of fracture ends) has often been suggested as an indication for surgery, a review found that people treated without surgery for shortening of mid shaft clavicle fractures did not affect outcomes.
A discontinuity in the bone shape often results from a clavicular fracture, visible through the skin, if not treated with surgery. Surgical procedures often call for open reduction internal latefixation where an anatomically shaped titanium or steel plate is affixed along the superior aspect of the bone by several screws. In some cases, the plate is removed after healing due to discomfort, to avoid tissue aggravation, osteolysis or subacromial impingement. This is especially important with a special type of fixation plate called hook plate. With anatomical plates plate removal is considered an elective procedure that is rarely necessary. An alternative to plate fixation is elastic TEN intramedullary nailing. These devices are implanted within the clavicle's canal to support the bone from the inside. Typical surgical complications are infection, neurological symptoms distal the incision (sometimes to the extremity), and
For breaks in the middle of the clavicle in children surgery resulted in faster recover but more complications. The evidence for different types of surgery for breaks of the middle part of the clavicle is poor as of 2015.
Surgery may be considered when one or more of the following is presents
* Comminution with separation (bone is broken into multiple pieces)
* Skin penetration (open fracture)
* Associated nervous and vascular trauma (brachial plexus or supraclavicular nerves)
* Nonunion after several months (3–6 months, typically)
* Displaced distal third fractures (high risk of nonunion)
* Although shortening (as a result of overlap of fracture ends) has often been suggested as an indication for surgery, a review found that people treated without surgery for shortening of mid shaft clavicle fractures did not affect outcomes.
A discontinuity in the bone shape often results from a clavicular fracture, visible through the skin, if not treated with surgery. Surgical procedures often call for open reduction internal latefixation where an anatomically shaped titanium or steel plate is affixed along the superior aspect of the bone by several screws. In some cases, the plate is removed after healing due to discomfort, to avoid tissue aggravation, osteolysis or subacromial impingement. This is especially important with a special type of fixation plate called hook plate. With anatomical plates plate removal is considered an elective procedure that is rarely necessary. An alternative to plate fixation is elastic TEN intramedullary nailing. These devices are implanted within the clavicle's canal to support the bone from the inside. Typical surgical complications are infection, neurological symptoms distal the incision (sometimes to the extremity), and nonunion
Nonunion is permanent failure of healing following a broken bone unless intervention (such as surgery) is performed. A fracture with nonunion generally forms a structural resemblance to a fibrous joint, and is therefore often called a "false j ...
of the bone (failure of the bone to properly fuse together).
Prognosis
Healing time varies based on age, health, complexity, and location of the break, as well as the bone displacement. For adults, one to several weeks of sling immobilization is normally employed to allow for pain relief, initial bone and soft tissue healing; teenagers require slightly less, while children can often achieve the same level in two weeks. During this period, patients may remove the sling to practice passive pendulum range of motion exercises to reduce atrophy in the elbow and shoulder, but they are often minimized to 15–20° off vertical. Depending on the severity of fracture, a person can begin to use the arm if comfortable with movement and no pain results. The final goal is to be able to have full range of motion with no pain; therefore, if any pain occurs, allowing for more recovery time is best. Depending on severity of the fracture, athletes involved in contact sports may need a longer period of rest to heal to avoid refracturing bone. A person should be able to return unrestricted to any sports or work by 3 months after the injury.Epidemiology
Clavicle fractures occur at 30–64 cases per 100,000 a year and are responsible for 2.6–5.0% of all fractures. This type of fracture occurs more often in males. About half of all clavicle fractures occur in children under the age of seven and is the most common pediatric fracture. Clavicle fractures involve roughly 5% of all fractures seen in hospital emergency admissions. Clavicles are the most commonly broken bone in the human body.History
Hippocrates, 4th century BC: From an ancient Egyptian text of approximately the 30th century B.C., in a copy known as the Edwin Smith papyrus, J. Breasted translation, case 35: All the cases in this text describe examination, prognosis, and (where applicable) treatment, in that order.References
External links
Details from AAOS
{{DEFAULTSORT:Clavicle Fracture Bone fractures Injuries of shoulder and upper arm Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate